Applications of MTP/MPO Cable Types in 5 Performances
The MTP/MPO system has proven to be an effective solution for cable congestion in data centers and businesses due to its scalability, dependability, and flexibility. To ensure that any transmitting signal from any active piece of equipment is routed to the receiving port of another active piece of equipment, the appropriate polarity must be maintained throughout the fiber network.
MTP/MPO cable types are distinguished by five characteristics: function, polarity, fiber count, fiber mode, and jacket rating.
1. Function
There are three MTP/MPO cable types that are well suited for high-density cabling networks that provide increased network capacity and flexibility: trunk cables, breakout cables, and conversion cables.
MTP/MPO Trunk Cables
MTP/MPO connectors (female/male) are used to terminate MTP/MPO trunk cables, which come in counts ranging from 8 to 144 fibers. These multifiber MTP/MPO trunk cables are frequently the best choice for building a structured cabling system, including the backbone and horizontal connectors like 40G-40G and 100G-100G direct connections.

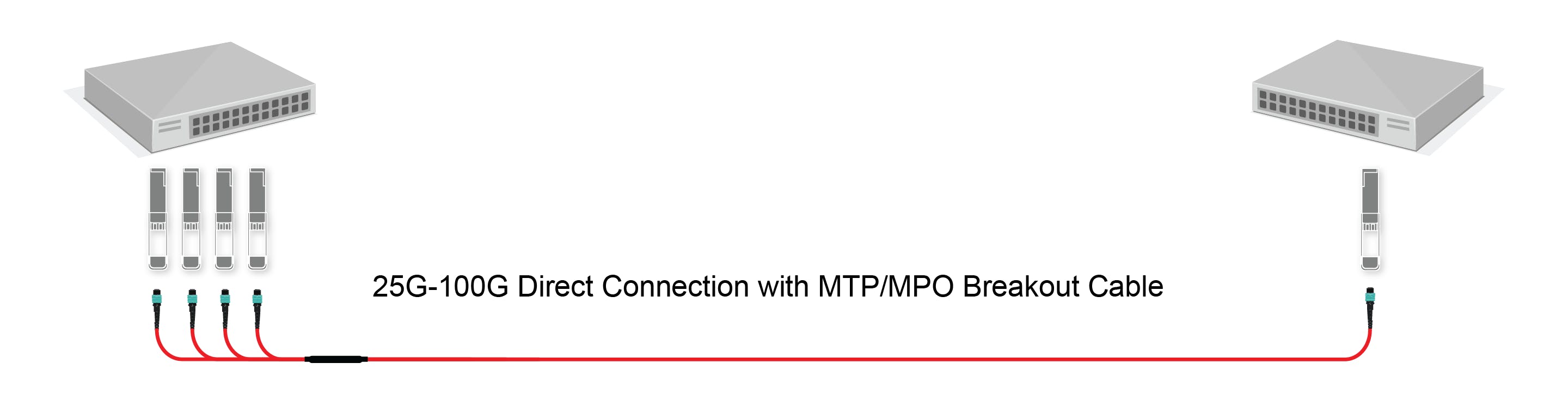
MTP/MPO Breakout Cables
MTP/MPO breakout cables (also known as harness cables or fanout cables) have a female/male MTP/MPO connector on one end and 4/6/8/12 duplex LC/FC/SC/ST connectors on the other. These breakout cables are typically used for short distance 10G-40G and 25G-100G direct connections, as well as connecting backbone assemblies to a rack system in high-density backbone cabling.
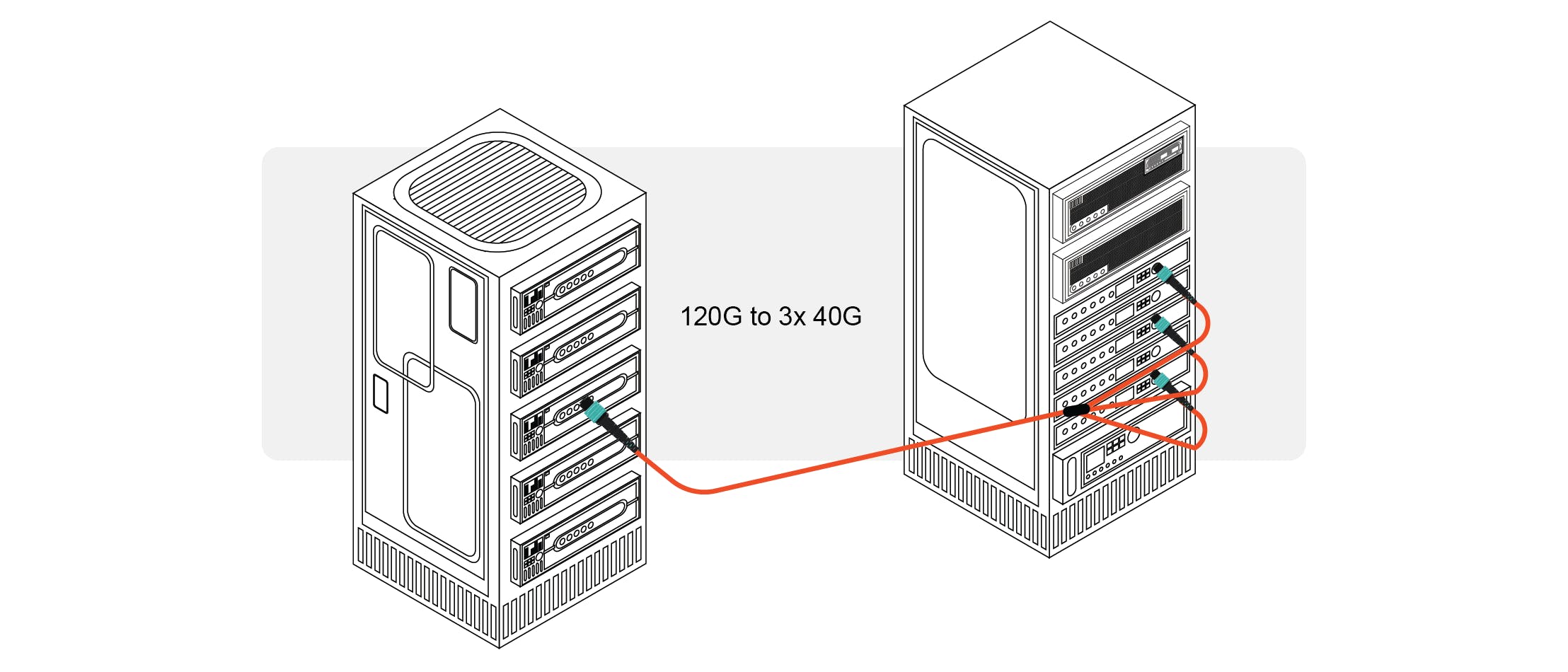
MTP/MPO Conversion Cables
Although they have a different fiber count and type, MTP/MPO conversion cables have the same fanout design as MTP/MPO breakout cables. The MTP/MPO connectors are used to terminate them on both ends and significantly increase the MTP/MPO cabling system's versatility. These are well-suited for connections at speeds of 10G-40G, 40G-40G, 40G-100G, and 40G-120G.
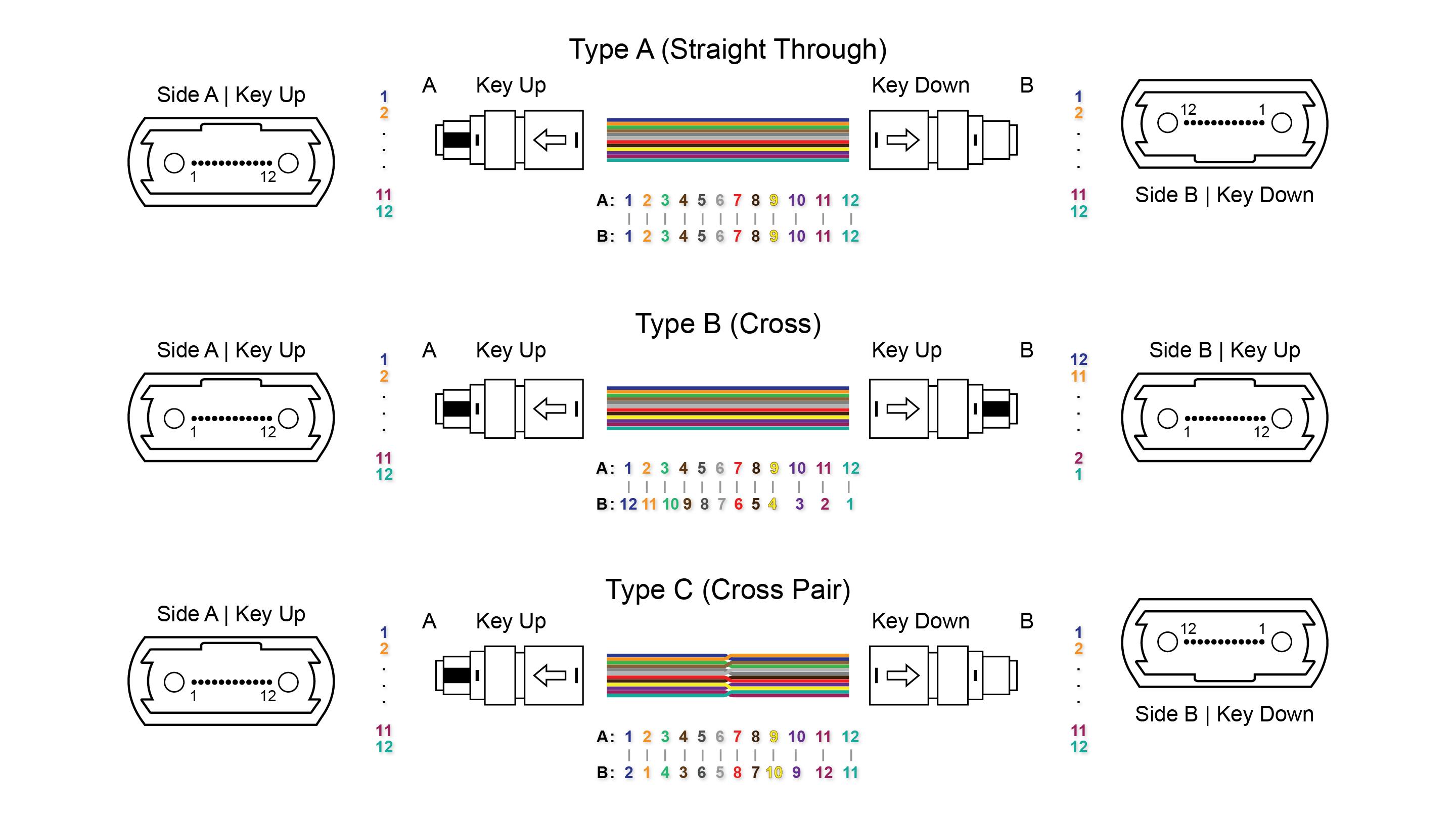
2. Polarity
The polarity of MTP/MPO cable types refers to the difference between the optical transmitters and receivers at both ends of the fiber link. Due to the unique design of MTP/MPO connectors, polarity issues must be addressed in high-density MTP/MPO cabling systems. There are three types of fiber polarity: Type A, Type B, and Type C.
- Type A (or straight-through method): The fiber located at position 1 (P1) on one end also arrives at P1 on the other end. A straight-through cable with a key-up MTP connector on one end and a key-down MTP connector on the opposite end. This makes the fibers at each end of the cable have the same fiber position.
- Type B (or reversed method): The fiber located at P1 on one end arrives at P12 at the other end, as it uses key-up connectors on both ends of the cable. The fiber locations are inverted at both ends as a result of this kind of array mating.
- Type C (or twisted pair method): The fiber at P1 on one end arrives at P2 on the opposite end, P2 arrives at P1, and so on for each pair of fibers. Type C cable (pairs flipped cable) resembles Type A cable in appearance, with one key-up and one key-down connector on each side. However, in Type C, each adjacent pair of fibers at one end is flipped at the other end.
3. Fiber Count
MTP/MPO cable types with different cores are classified as 8/12/24 cores and are typically used for 40G/100G transmission. The most recent 16-fiber cables are specifically designed for 400G short-reach cabling in Hyperscale data centers.
- 8-fiber MTP/MPO cables – transmit the same data rates as 12-fiber cables with lower cost and insertion loss, making them more cost-effective.
- 12-fiber MTP/MPO cables – the first and most widely used solution in 10G-40G, 40G-100G connections.
- 24-fiber MTP/MPO cables – commonly used to connect CFP-to-CFP transceivers. Recommended to use for migration to 40/100/400GbE.
- 16-fiber MTP/MPO cables – combine multiple 8-fiber parallel transceivers and interface directly to upcoming 16-fiber parallel fiber links like 400G QSFP-DD and OSFP.
4. Fiber Mode
MTP/MPO cable types include multi-mode OM3/OM4 cables and single mode OS2 cables.
- Multi-mode OM3/OM4 MTP/MPO cables are suitable for short-distance transmission, with a maximum transmission distance of 100m or 150m.
- Single mode OS2 MTP/MPO cables are ideal for long-distance transmission in MANs (metropolitan area network) and PONs (passive optical networks).
- OS2 has a higher bandwidth than OM3/OM4 because it has less modal dispersion.
To learn more about fiber mode cables read Fiber Optic Cable Types: Single Mode vs. Multi-mode Fiber Cable for more information.
| Products | OM3 | OM4 | OS2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | 850nm | 850nm | 1310nm/1550nm |
| Max Transmission Distance | 100m | 150m | 200km |
| Application | Buildings, Campus | Buildings, Campus | Carrier Networks, MANs, & PONs |
5. Jacket Rating
MTP/MPO cable jackets are classified as LSZH (Low Smoke Zero Halogen), OFNP (Optical Fiber Nonconductive, Plenum), CMP (Communications Multipurpose Cable, Plenum), and so on based on different fire rating requirements.
- LSZH MTP/MPO cables – free of halogenated materials protects personnel and equipment during fires and makes them suitable for use in enclosed spaces.
- OFNP MTP/MPO cables – have no electrically conductive elements and are designed with the highest fire rating, allowing them to be installed in ducts and other building airflow spaces.
- CMP MTP/MPO cables – suitable for plenum spaces where air circulation for heating and air conditioning systems is facilitated.
After determining the five components of MTP/MPO cables, it is easier to select the network connection solution that best meets their needs. Since they are popular for high-density cabling in data centers, they can greatly increase network capacity, save a lot of space, and simplify cable management.
